What Does Remainder Mean In Long Division
Usually we write this concisely as follows. However the technique is the same.

Math Worksheets Division With Remainders Math Worksheets Long Division Worksheets Division Worksheets
The quotient is how many times the divisor fits into the dividend in this case 3.

What does remainder mean in long division. As often as possible well avoid computation on GMAT problems by estimating and looking for shortcuts. For example 103 9 remainder 1. The same goes for polynomial long division.
The amount left over when you divide two numbers. Upper and Lower Bound Tests for Real Zeros Suppose fx is divided by x - k using synthetic division. Remainder refers to the remaining part after the completion of the division process.
Whatever else was left if anything was your remainder. Also if you divide the number 20 with a number 3 the quotient is 6 and the remainder is 2. This is the currently selected item.
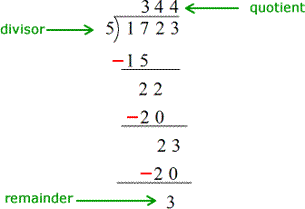
Long Division and Remainders Long division is the process of writing out the division of one number by another. When you divide 11 by 2 you end up with 1 left over as shown in the worked out long division below. The conventions used when preforming long division this way regarding the placement of the terms of the polynomials vary.
In this case the remainder remains behind because it is not needed. We can still use our. The remainder is always less than the divisor.
In polynomial terms since were dividing by a linear factor that is a factor in which the degree on x is just an understood 1 then the remainder must be a constant value. In algebra the polynomial remainder theorem or little Bézouts theorem named after Étienne Bézout is an application of Euclidean division of polynomials. For regrouping in the subtraction part you just need to be very careful with how you write it.
If a number cant be equally divided among a divisor theres a leftover thats the remainder. What is a remainder. To learn about Long Division of Polynomials Remainder and Factor Theorems Synthetic Division Rational Zeros Theorem.
It can be greater than or lesser than the quotient. When 41 is divided by 7 the quotient is 5 and the remainder is 6. It states that the remainder of the division of a polynomial by a linear polynomial.
Make the 1 that you small and try to put it below the first subtraction line to keep things tidy. For the remainders whatever is left after the subtracting is the remainder. Once you got to something that the divisor was too big to divide into youd gone as far as you could so you stopped.
Dividing by a 2-digits. This example is translated into maths the remaining 1 pen is the remainder. You know from long division of regular numbers that your remainder if there is one has to be smaller than whatever you divided by.
Your remainder you write it on top of the division bar with an r in front of it like this. If we divide 5 pens among 4 children equally we are left with 1 pen. In fact when it comes to division problems there are 4 possible ways to interpret the remainder depending on the specific situation where the division operation is being used.
If your remainder is more than your divisor you need to go back and check your division because it is incorrect. When one number divides another number completely the remainder is 0. You will need to be able to perform long division on the GMAT.
Leaving the Remainder - This is the most basic form of interpreting the remainder. When your division ends with a remainder you must make sure that your remainder is less than your divisor. The remainder of a division problem is an interesting part of.
Lastly the remainder is whats left over or 8. Therefore 10 mod 3 1. Introduction to dividing by 2-digits.
If k 0 and every number in. Long division with remainders. Long division with remainders.
If the remainder is greater than the divisor it means that the division is incomplete. The quotient 𝑞 𝑥 is the expression above the line and the remainder is the expression at the bottom. The divisor in a division equation is also known as the modulus giving us the name of the operation.
Its much like how you knew when to stop when doing the long division before you learned about decimal places. For instance lets examine 11 2.

Interpreting Division Remainders Hands On Centers Or Remote Learning Task Cards Math School Math Division Teaching Math

Division Poster Math Division Math School Math Vocabulary

Division Word Problem Scoot Division Word Problems Word Problems Interpreting Remainders

World S Longest Long Division Problems Worksheets Free Printables Math Worksheets Division Division Worksheets Math Worksheets Division Practice
Polynomial Long Division Chilimath

Interpreting Remainders In Division Word Problems Google Search Math Operations Interpreting Remainders Math Instruction

How To Do Long Division In 6 Steps With Pictures Prodigy Education

Pin By Claire Mclendon On Teaching Math Anchor Charts Math Education Math

Long Division Worksheet Packet With Remainder 5 Pages Division Worksheets Long Division Long Division Worksheets

Use Long Division To Divide Polynomials College Algebra

Long Division By Multiples Of 10 With Remainders Large Print Long Division Division Worksheets Math Drills

Learn How To Interpret The Remainder In 3 Different Ways Ignore It Round It Or Report It As A Fraction Or Decim Math Resources Math Notebook Elementary Math

Remainder In Math Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Worksheets For Division With Remainders

How To Do Polynomial Long Division 9 Powerful Examples Rational Expressions Polynomials Math Methods

Interpreting The Remainder With Dab Interpreting The Remainder Anchor Chart Interpreting Remainders Interpreting Remainders Anchor Chart Math Expressions

Christmas Gifts Long Division With Remainders Task Cards Task Cards Student Christmas Gifts Students Christmas

How To Do Long Division In 6 Steps With Pictures Prodigy Education

What Is Remainder Remainder With Long Division Examples